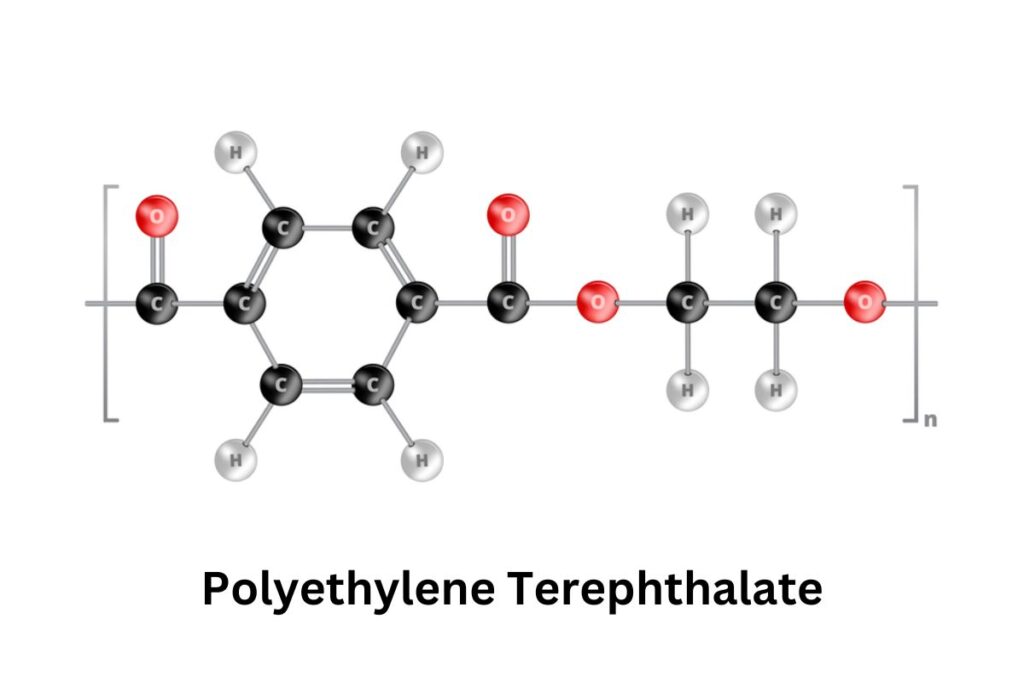
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) film, commonly known as PET film, has become an indispensable material in a wide array of industries. PET film is a high-performance thermoplastic polymer widely used in various industries. Known for its exceptional mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties, PET film serves as a preferred material in packaging, electrical insulation, and industrial applications. Its versatility allows it to be used in rigid and flexible forms, making it a crucial component in modern manufacturing.
Brief History and Development
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) was first synthesized in the early 1940s by British chemists John Rex Whinfield and James Tennant Dickson at the Calico Printers’ Association in the United Kingdom. Their research led to the development of Terylene, the first polyester fiber, which was later commercialized by Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI). Around the same time, DuPont in the United States independently developed Dacron, another polyester fiber, marking the beginning of PET’s widespread use in textiles.
While PET was initially developed as a fiber-forming polymer for the textile industry, its potential as a film-forming material was recognized later. In the 1950s, advancements in polymer processing led to the development of biaxially-oriented PET film (BOPET), a process that significantly enhanced the film’s strength, clarity, and barrier properties. One of the first companies to commercialize BOPET film was DuPont, which introduced it under the brand name Mylar® in 1952.
The superior properties of BOPET—such as high tensile strength, thermal stability, moisture resistance, and excellent barrier properties—quickly made it a preferred material for industrial applications, packaging, electrical insulation, and specialty coatings. By the 1960s and 1970s, PET film was being widely used in flexible food packaging, audio and video tapes, and industrial laminates.
The 1980s and 1990s saw significant improvements in PET film manufacturing, including the development of co-extrusion technologies, metallized PET films, and high-barrier coatings, which further expanded its applications. These advancements made PET film essential in industries such as pharmaceutical packaging, high-performance insulation, and advanced electronics.
In recent decades, growing environmental concerns have driven innovations in PET recycling and sustainability. The introduction of recycled PET (rPET) and advancements in chemical recycling technologies have made PET one of the most recyclable and sustainable plastic films in the world. Today, PET film continues to be a key material in packaging, industrial applications, and emerging technologies like flexible electronics, solar panels, and medical diagnostics.
From its early days as a textile fiber to its dominance in modern plastic film applications, PET has evolved into a high-performance, versatile, and environmentally sustainable material that continues to drive innovations across multiple industries.
Properties and Characteristics of PET Film
PET film is a high-performance thermoplastic polymer known for its exceptional strength, chemical resistance, clarity, and environmental stability. Due to its versatile properties, it is widely used in packaging, industrial applications, electronics, and printing. Below is a detailed breakdown of its key characteristics.
1. Physical and Chemical Properties
- High Tensile Strength & Durability: PET film is renowned for its superior tensile strength, meaning it can withstand significant mechanical stress without tearing or breaking. Even in thin gauges, it maintains high impact resistance, making it ideal for industrial applications that demand durability, such as lamination films, flexible circuits, and protective coatings.
- Excellent Optical Clarity: PET film can be manufactured with high transparency and low haze, making it suitable for applications where visibility and aesthetics are crucial, such as packaging. In addition, PET films can be modified with coatings to enhance anti-glare or anti-fog properties.
- Superior Dimensional Stability: Unlike many other plastic films, PET exhibits low shrinkage and excellent dimensional stability across a wide temperature range. This property makes it a preferred material for precision printing, graphic overlays, and high-precision electronic components.
- Exceptional Chemical Resistance: PET film is highly resistant to a wide range of chemicals, solvents, and oils, making it suitable for packaging sensitive products such as pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and food items. Unlike PVC or polycarbonate films, PET does not degrade when exposed to acids, alcohols, and hydrocarbons, ensuring long-term stability.
- Effective Barrier Properties: PET film acts as a strong barrier against moisture, gases, and contaminants, extending the shelf life of packaged products. Its low permeability to oxygen and carbon dioxide makes it particularly useful in food packaging and pharmaceutical applications where product integrity is essential.
2. Strength, Durability, and Flexibility
- High Strength-to-Thickness Ratio: PET film offers exceptional strength even in thin films, reducing material usage while maintaining robust performance. This makes it highly cost-effective and eco-friendly in applications such as flexible packaging and industrial laminates.
- Puncture & Tear Resistance: Compared to polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene (PE) films, PET exhibits significantly higher tear resistance and mechanical toughness. This ensures that the material remains intact under mechanical stress, making it ideal for applications such as security labels, protective coatings, and industrial tapes.
- Flexibility & Formability: Despite its high strength, PET film retains flexibility, allowing it to be easily thermoformed, laminated, or printed upon. This makes it an excellent choice for folding cartons, shrink labels, and curved electronic displays.
Applications of PET Film in Packaging
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) film is a crucial material in the packaging industry due to its durability, transparency, and protective properties. It is widely used in various packaging applications, ensuring product safety, extended shelf life, and visual appeal. Below are the key applications of PET film in packaging:
1. Flexible Food Packaging
PET film is extensively used in flexible packaging to protect food products from moisture, oxygen, and contaminants. Some common applications include:
- Snack and Confectionery Wrappers: PET film provides excellent barrier properties, preventing oxidation and preserving freshness.
- Laminated Pouches: Used for packaging processed foods, sauces, and ready-to-eat meals, offering high strength and heat-sealing capabilities.
- Bakery and Dairy Packaging: Its transparency ensures product visibility, while its moisture barrier prevents spoilage.
2. Lidding Films and Sealing Applications
PET film is a preferred material for lidding applications due to its heat resistance and strong sealability. Examples include:
- Dairy Product Lids: Used for yogurt, cheese, and dessert containers to ensure airtight sealing.
- Microwaveable and Oven-Safe Packaging: Heat-resistant PET lidding films allow safe reheating of ready meals.
- Tamper-Evident Seals: Provides secure seals for food and beverage containers to ensure consumer safety.
3. Beverage Bottle Labels and Shrink Sleeves
PET film is widely used in labeling applications due to its moisture resistance and printability. Common uses include:
- Wrap-Around Labels: Applied to water, juice, and soft drink bottles, offering high durability and clarity.
- Shrink Sleeves: PET shrink films provide 360-degree branding on beverage bottles, increasing shelf appeal.
4. High-Barrier Packaging for Sensitive Products
PET film is often metallized or laminated with other materials to enhance barrier properties, making it ideal for:
- Coffee and Tea Packaging: Prevents oxidation and moisture absorption to maintain freshness.
- Snack and Dry Food Pouches: Used for chips, nuts, and cereals, offering superior gas and aroma barriers.
- Vacuum-Sealed Packaging: Ideal for meat, cheese, and perishable foods requiring extended shelf life.
5. Pharmaceutical and Medical Packaging
Due to its chemical resistance and sterility, PET film is widely used in pharmaceutical applications:
- Blister Packaging for Pills and Capsules: Protects medications from light, moisture, and contamination.
- Sterile Medical Packaging: Used for syringes, surgical instruments, and diagnostic kits.
Advantages and Disadvantages of PET Film
PET film offers several advantages, making it a preferred material across various industries. Its high strength, durability, and excellent barrier properties protect products from moisture, oxygen, and contaminants, ensuring extended shelf life. Additionally, PET film is lightweight yet strong, reducing transportation costs without compromising performance. One of its key benefits is recyclability, allowing for reuse in various applications and supporting sustainability efforts. It is also cost-effective, offering a balance between performance and affordability compared to some alternative materials. Furthermore, PET film exhibits good thermal and chemical resistance, making it suitable for food packaging, pharmaceutical packaging, and industrial packaging.
Despite its benefits, PET film has some limitations. It is not biodegradable, meaning improper disposal can contribute to environmental concerns if not recycled properly. While it offers moderate moisture resistance, it may not be sufficient for highly moisture-sensitive applications compared to specialized films. PET film is also sensitive to prolonged UV exposure, requiring stabilizers or protective coatings to prevent degradation over time. Additionally, processing PET film requires specialized equipment, increasing production costs for extrusion, lamination, and recycling. Despite these drawbacks, PET film remains a widely used and versatile material, especially when combined with proper recycling and treatment methods.
PET Film vs. Other Plastic Films
When selecting the right material for packaging and industrial applications, it is essential to compare PET film with other commonly used plastic films like PVC, polycarbonate, BOPP, and LDPE. Each material has unique properties that make it suitable for specific uses.
- PET Film vs. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): PET film is generally considered more environmentally friendly than PVC, as PVC contains chlorine and releases harmful substances when burned. Additionally, PET offers better chemical resistance and food safety, making it a preferred choice for food and pharmaceutical packaging. While PVC is more flexible and lower in cost, it lacks PET’s superior strength and thermal stability, which are essential in high-performance packaging applications.
- PET Film vs. Polycarbonate (PC): Polycarbonate is highly impact-resistant and can withstand extreme temperatures, making it suitable for safety equipment, automotive applications, and electronic housings. However, PET film is more cost-effective, has better moisture resistance, and provides excellent clarity, making it ideal for packaging, labeling, and protective films. PET’s chemical resistance also gives it an advantage in applications where exposure to solvents and oils is a concern.
- PET Film vs. BOPP (Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene): BOPP is widely used in food packaging and labels due to its low cost and good moisture resistance. However, PET film offers better tensile strength, gas barrier properties, and heat resistance, making it a superior choice for applications like retort packaging, lidding films, and high-performance laminates. BOPP lacks the durability and high-temperature resistance that PET provides, which is crucial for heat-sealed packaging and industrial applications.
- PET Film vs. LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene): LDPE is known for its flexibility and softness, making it a good option for stretch wraps, plastic bags, and squeezable bottles. However, PET film offers much higher structural integrity, transparency, and barrier properties, making it the preferred choice for rigid packaging, tamper-evident labels, and food-safe applications. While LDPE is more pliable and cheaper, it does not provide the same level of strength, thermal stability, or gas barrier protection as PET.
FAQ
1. Is PET film safe for food packaging?
Yes, PET film is FDA-approved for food contact and widely used in food packaging.
2. Can PET film be recycled?
Yes, PET film is fully recyclable and can be repurposed into new products.
3. What makes PET film different from other plastic films?
PET film offers superior strength, clarity, and barrier properties compared to many other plastic films.
4. Does PET film degrade over time?
While durable, PET film can degrade under prolonged UV exposure if not properly stabilized.
5. What industries benefit most from PET film?
Industries such as packaging, electronics, medical, and printing rely on PET film for its unique properties.
6. How does PET film contribute to sustainability?
By being fully recyclable, PET film helps reduce plastic waste and supports the circular economy through rPET production.